Share This Article
The world’s largest ITER fusion reactor to be launched in 15 years
ITER is the world’s largest fusion reactor. It is an experimental project designed to demonstrate the machine’s potential for commercial use.
The reactor’s assembly began in France in 2020. At that time, the project authors promised a launch. However, the plant did not start operating on the scheduled date, even though the assembly had been completed. Now, it has become known that ITER will start functioning only in 2039.
Thirty-five countries participated in the development and installation of ITER, including the EU countries, the UK, the USA, China, and others. Scientists have equipped the reactor with the world’s most powerful magnet, which allows it to create a magnetic field around itself. In terms of power, it is 28 thousand times stronger than the one around the planet.
The project cost US$28 billion. The authors initially expected to spend US$5 billion, but some factors changed their plans. The price increase delayed the start of the project by 15 years.
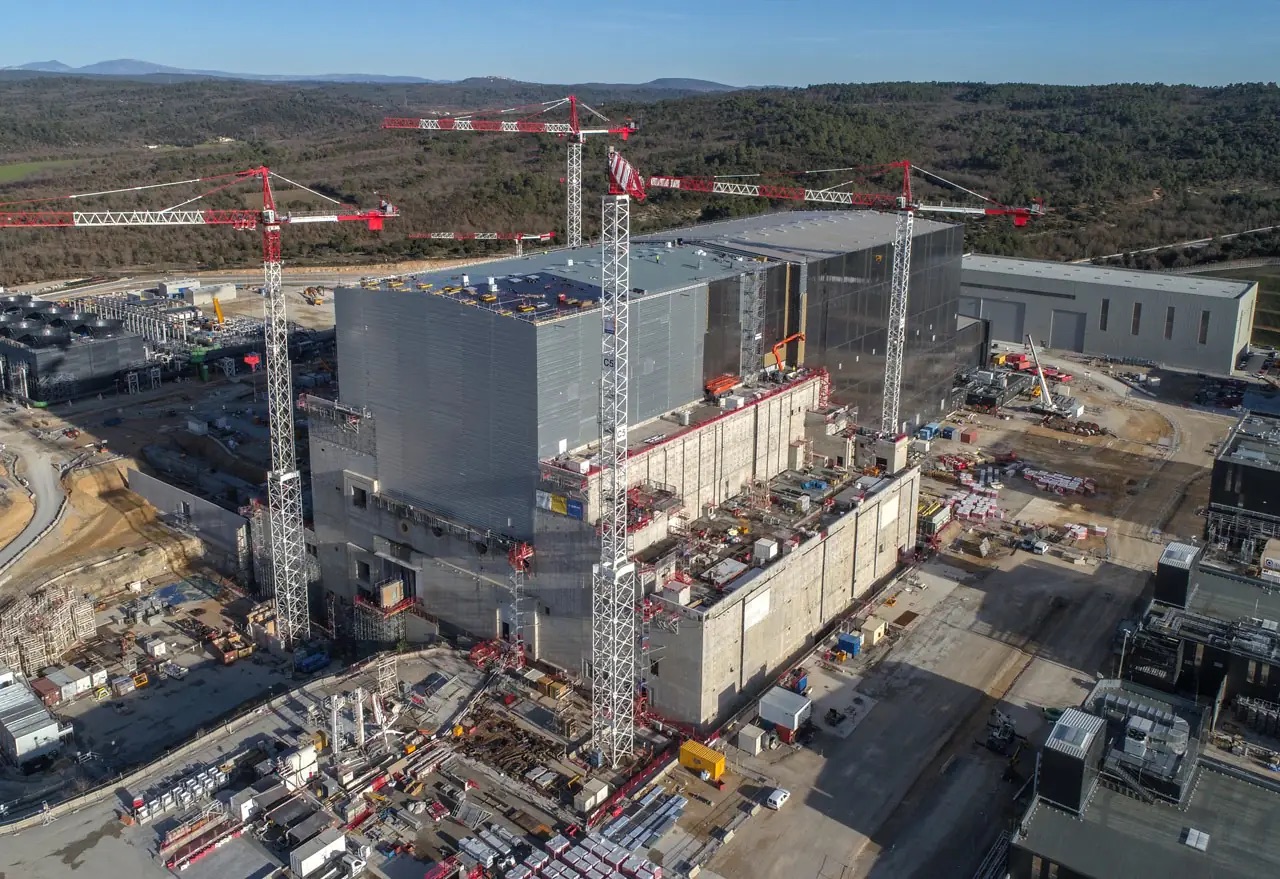
Features of the installation
The reactor weighs 23 thousand tonnes and is 30 metres high. A 180-hectare complex will house the machine. In addition to ITER, there are facilities to monitor its operation.
This type of reactor is called a tokamak. There are two similar devices in the world – in the UK and Japan – but they are much smaller than ITER. Tokamaks have a number of features that distinguish them from other nuclear products:
- tokamaks combine the capabilities of magnets, heaters and other elements;
- this approach allows thermonuclear reactions to take place in ultra-hot plasma;
- the process releases energy;
- the magnetic field holds the charged particles inside the vessel and gives them momentum to rotate;
- the reactor vessel is shaped like a bagel, allowing the particles to combine and produce fusion energy.
The size of the reactor is essential. Large plants have good insulation. This will allow the particles created by fusion to last longer. As a result, tokamaks produce more energy than smaller devices.
It is important to maintain a temperature higher than the sun’s when using this type of reactor. At the same time, the tokamak operates at low pressure. In addition, the characteristics of the plasma have to be regularly monitored for nuclear fusion to take place.
Despite their high power, ITER and similar reactors cannot yet be used for full-scale energy production. This would require an increase in power by about 5. The launch of ITER is intended only to demonstrate the potential and carry out research to improve the process.

